In this article, we will be talking about Declaring VBA Variables. Variables are essential elements of programming. Using and managing variables are one of the musts while creating a project. I will try my best to tell it as simple as possible. Reminder: You can find other articles about VBA on our blog. 👍🏻
About Declaring VBA Variables
Variables are usually used to store a data and use it when necessary. They are usually separated into two classes. Global variables and Local variables. Global variables can be used by all the functions of the program, but the local variables are used by the functions that have declared them.
It can be called back, reassigned or fixed during the execution of a procedure, function or module.
Declaring a variable will enable you to indicate the names of the variable you’ll use and the data type the variable will contain.
For example, if Result = 10, the variable Result can be declared as Integer Whole Number .
We usually name the variables in a short and easily remembered way. The most frequently used variable names are one character names like i, a, n, x ,y ,z, s so that it is easy to write in the code. If the variable name is a name that you can remember while using in the code, the probability of making a mistake while writing the code decreases.
Now we can move on to the declaring part.
The syntax concerning declaring variables is usually like this.
Dim variable_name [(stringsize)] As type
Public variable_name[(stringsize)] As type
Static variable_name[(stringsize)] As type
Along side this general declaring, the declaring methods below can be used as well.
- Declaring with Dim
- Declaring with Data Indicators (Abbreviations)
- Declaring with DEF
Declaring with Dim
It is the most known and used VBA Variable Declaring method.
We indicated the syntax Syntax below. Let’s make it clear with a few examples. Let’s say that we will declare a variable named row to use in the rows (cells) in the A column. Since the row numbers are whole numbers, we can used one of the whole number types we’ve indicated in our Data Types article. It would be better to use the variable data type depending on the row number we’ll get controlled or the maximum number that can be in the cell.
As well as we can use as Number or Whole Number, we have 3 basic variable data types: Byte, Integer and Long. If the number we’ll assign to the row variable is 255 or less, then we can use the Byte variable data type. If the number we’ll assign to the row variable is between –32767 and+32768, then we can use the Integer variable data type. If it can be a bigger whole number, then we should use the Long variable data type. If a bigger number than what the variable can contain is sent, that the Overflow error occurs. And if a text data is sent to a variable that was determined as number, Type Mismatch error occurs.
Let’s give a few examples of declaring variables with Dim:
Sub PEAKUP()
Dim row As Long
Dim column As Byte
Dim text As String
Dim start As Date
Dim money As Currency
Dim object As Object
row = 15
column = 5
text = "Excel Turkey Forum"
start = "24.06.2018"
money = 300
Set object= ActiveSheet
End Sub
We can write each variable one by one in different rows like that, but we also can write them side by side like this. We just need to put Dim in the beginning and put a comma between each variable.
Sub PEAKUP()
Dim row As Long, column As Byte, text As String
Dim start As Date, money As Currency, object As Object
End Sub
We need to be careful about this here: Some users make a mistake and declare incorrectly.
If you write the code I gave above like this one below, I mean if you start with Dim and think that you’ve declared the first variable and not declare the other variables with the suitable variable data types. Since in the “column”, “text” variable the data type is not stated, Byte and String are not indicated but Variant is -which is undefined data type. Since in the first variable I’ve declared with Dim, you declare the data type in the first variable. So, it doesn’t mean that you declare the next variables as well. You need to state the data type of each variable one by one.
Declaring with Data Identifiers (Abbreviations)
Abbreviations
They are also known as Type Indication suffixes.
They are not used much but they help to save in codes.
It is also possible to tell a variable type by adding a special character to the end of the variable name in VBA.
Dim number% 'Integer
Dim longnumber& 'Long
Dim sum! 'Single
Dim subtotal# 'Double
Dim payment@ 'Currency
Dim name$ 'String
Dim longestnumber^ ' 64 bit LongLong
Data Type Abbreviation Characters
VBA
, as a fast way of declaring data type, lets you add a character in the name of a variable.
This method shouldn’t be used to declare variables and it can be used for retrospective purposes only.
The row below will declare a Double data type and a variable.
Dim dDouble#
But it is better for this row to be declared with the “As” keyword.
Dim dDouble As Double
Data Type Abbreviation/ Suffixes
If you you abbreviations, you don’t have to declare the type.
If you use the % expression, you don’t need to write “As Integer”.
These abbreviations can be helpful to get available information to Variants.
For example: count =10#
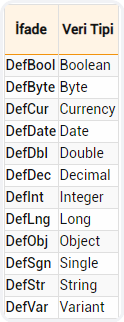
Declaring with DEF
We can declare our variables with different methods like we mentioned, one of these methods is declaring with DEF.
This declaration is usually done free from the procedure at the top of the code window.
We can abbreviate and declare the data type we use as variable like below.
The letter that comes after Def+Type indicated that the variables starting with that letter belong to that type.
Let’s see an example that shows the difference between declaring with Def and Dim.
First, let’s declare our variables like this with Dim.
Sub PEAKUP()
Dim row As Integer, column As Integer
Dim text As String, letter As String, word As String
Dim date As Date, start As Date
Dim number As Double, price As Double
row= 10
column= 5
text = "PEAKUP"
letter = "E"
word = "Book"
date = "24.06.2018"
start = "14.12.1980"
number = 1453.48
price = 5647.15
End Sub
Now, let’s do the same declaration with Def.
DefInt R
DefStr L, W, T
DefDate S, D
DefDbl P, N
Sub PEAKUP()
row = 10
column = 5
text = "PEAKUP"
letter = "E"
word = "Book"
date = "24.06.2018"
start = "14.12.1980"
number = 1453.48
price = 5647.15
End Sub
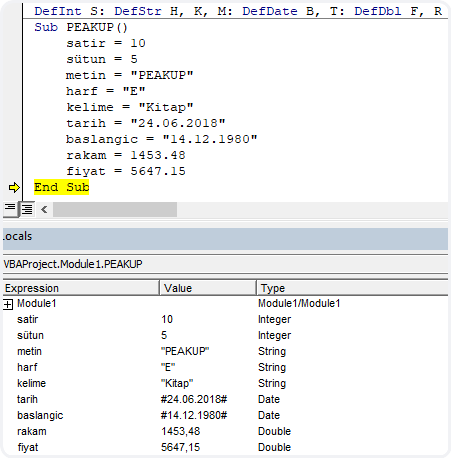
As you see, we got to indicate the type by using the initials and declare the variables. At this point, you want the variable declarations not to take too much space and be seen in less rows. As indicated below, you can write the Def rows in a row next to one other with a colon (:).
DefInt R: DefStr L, W, T: DefDate S, D: DefDbl P, N
Sub PEAKUP()
row = 10
column = 5
text = "PEAKUP"
letter = "E"
word = "Book"
date = "24.06.2018"
start = "14.12.1980"
number = 1453.48
price = 5647.15
End Sub
By the way, you can easily follow and evaluate the names, values and types of all variables from Locals Window.
You can take a look at the Microsoft Docs page for more information.
See you in other articles, bye.🙋🏻♂️
You can share this post with your friends and get them informed as well. 👍🏻







 PowerPoint
PowerPoint